When you need to measure the current in a circuit, you can use a shunt resistor, also known as a current shunt resistor. Shunt resistors typically have a very low resistance value, much smaller than that of the circuit under test. This ensures that the power shunt resistor has very little effect on the overall circuit. Selecting the proper current shunt resistor resistance value can be determined based on the expected current range and required measurement accuracy.
Shunt resistors are widely used in various fields. Ammeter Shunt electronic can measure the current accurately and reliably, and realize the control and protection of the circuit.
Flexibility - Interchangeable shunts are designed to allow for flexibility in current range measurements. With interchangeable shunts, users can easily switch out the shunts to measure different current ranges, eliminating the need for multiple devices.
Accuracy - Interchangeable shunts typically provide high accuracy current measurement across a wide range of currents. This is particularly useful for applications where there are wide variations in current flow.
Ease of Use - Interchangeable shunts are easy to install and use, requiring minimal technical expertise to operate. This makes them ideal for use in a variety of settings, including industrial, laboratory, and scientific environments.
Cost Effective - Interchangeable shunts are a cost - effective solution for current measurement applications. As they can be easily swapped out, there is no need to purchase additional devices when measuring different current ranges.
Wide Range of Options - Interchangeable shunts are available in a wide range of values, making it easy to find a shunt that suits the specific needs of a particular application.
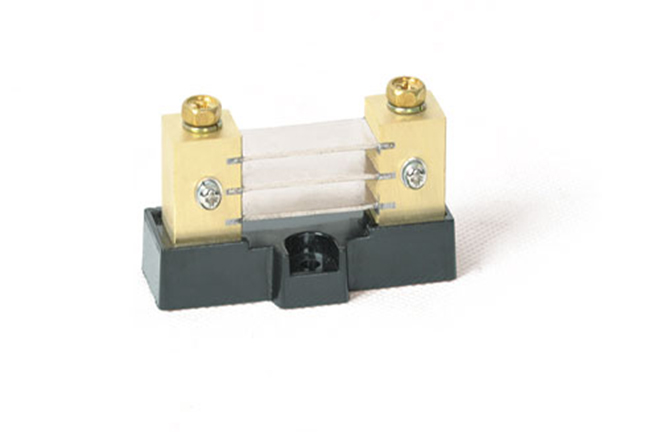

Dongya Interchangeable shunts are often used in electrical circuits to measure current. When selecting an interchangeable shunt, the following factors should be considered.
Shunt Accuracy: Make sure that the current reading taken from the shunt is as close as possible to the actual current in the circuit.
Shunt Resistor: The lower the resistance value, the better the sensitivity, but it also results in a larger voltage drop across the shunt.
Shunt Operating Current: Make sure the shunt is capable of measuring the maximum current of the circuit.
Temperature Coefficient: Consider any temperature changes in the application and select the shunt that best fits the expected temperature range.
Current Waveform: Consider the type of current waveform in your circuit, whether it is AC, DC, or pulsed.
Shunt Material: The shunt material must have a low temperature coefficient of resistance and low thermal resistance.
GET A QUOTE